Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: RSS
By Cary Blum MD, Marty Fried MD and Shreya P. Trivedi MD; Illustration by Mike Natter MD. Quiz yourself on the 5 Pearls we will be covering:
- How good is a urine dipstick, urinalysis and UACR in detecting albuminuria? (1:42)
- What are some conditions that lead to transient proteinuria? What is the appropriate interval to recheck and how should be it be repeated? (5:14)
- Who should be screened for albuminuria and can it prognosticate risk for cardiovascular mortality? (7:47)
- Does increasing RAAS inhibition improve renal outcomes? (10:57)
- Throwback Question: How do you prescribe oral iron and what tips do you tell your patients? (13:11)
Subscribe to CORE IM on any podcast app! Follow us on Facebook @Core IM || Twitter @COREIMpodcast || Instagram @core.im.podcast. Please give any feedback at COREIMpodcast@gmail.com.
Pearl 1
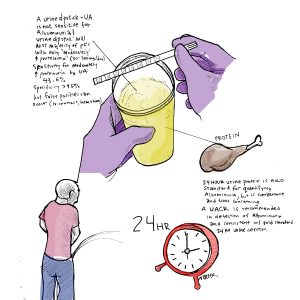
- The UA and urine dipstick is not sensitive for albuminuria.
- A urine dipstick will miss the majority of people with “moderately increased proteinuria” (30-300mg of albumin/day).
- Sensitivity for moderately increased proteinuria by UA: 43.6%
- Specificity of a UA is quite good (>95%) but false positives can occur in the setting of recent IV contrast, very alkaline urine, and gross hematuria
- 24 hour urine protein is the gold standard for quantifying albuminuria, especially for patients at the extremes of body weight, but is cumbersome and time-consuming.
- A urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR) is recommended in detection of albuminuria and consistent with the gold standard 24 hour urine collection.
- Dividing the urine albumin with urine creatinine is an attempt to adjust for the concentration of the urine on that particular sample, which varies throughout the day.
Pearl 2
- Transient proteinuria is benign and should always be ruled out. Defer testing if the pt has a strenuous exercise, febrile illness or UTI or other causes of transient proteinuria.
- Orthostatic proteinuria is a benign condition in which albuminuria is present when standing but disappears when supine. These conditions are benign and require no treatment or further monitoring.
- A good approach to a finding of proteinuria is to repeat the test in 3 months with a urine sample from the first morning void. Instruct patient to void before bed, then collect sample from first morning void.
Pearl 3
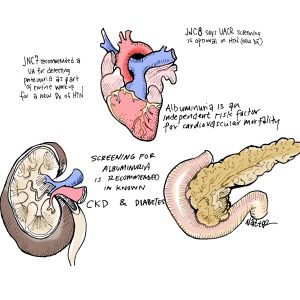
- Albuminuria is an independent risk factor for CV mortality.
- Screening for albuminuria is recommended in known CKD and diabetes
- In non-diabetic population, recommendations for screening are less established, but screening likely to be helpful when directed toward populations at highest risk, such as the elderly or pt’s with hypertension.
Pearl 4
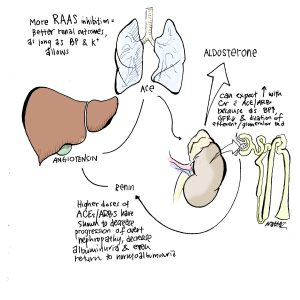
- More RAAS inhibition = better renal outcomes, as long as blood pressure and K+ allows.
- Higher doses of ACE/ARBs have shown to decreased progression to overt nephropathy, decreased the amount of albuminuria and even return to normoalbuminuria.
Pearl 5
- When choosing a dose, one should consider the pharmacology of hepcidin-induced malabsorption and balance this with the patient’s side effect burden. There is more evidence to suggest every other day oral iron dosing.
- Patients should be instructed to NOT take it with food and if possible with vitamin C or citrus food.
Many thanks to Dr. David Goldfarb for peer-reviewing this podcast!
References
- Park, JI, et. al. Comparison of urine dipstick and albumin:creatinine ratio for chronic kidney disease screening: A population-based study. PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0171106
- Zelmanovitz T, Gross JL, Oliveira JR, Paggi A, Tatsch M, Azevedo MJ: The receiver operating characteristics curve in the evaluation of a random urine specimen as a screening test for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 20:516-519, 1997
- Vehaskari VM, Rapola J. Isolated proteinuria: analysis of a school-age population. J Pediatr. 1982;101(5):661.
- Saydah, Sharon H., et al. “Albuminuria prevalence in first morning void compared with previous random urine from adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2009–2010.” Clinical chemistry 59.4 (2013): 675-683.
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003; 42: 1206-52.
- Boulware LE, Jaar BG, Tarver-Carr ME, Brancati FL, Powe NR. Screening for proteinuria in US adults: a cost-effectiveness analysis. JAMA. 2003;290(23):3101.
- Parving HH, Lehnert H, Bröchner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Irbesartan in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):870.
- Burgess E, Muirhead N, Rene de Cotret P, Chiu A, Pichette V, Tobe S. Supramaximal dose of candesartan in proteinuric renal disease. SMART (Supra Maximal Atacand Renal Trial) Investigators. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(4):893. Epub 2009 Feb 11.